WHAT IS ASTIGMATISM?
Your vision is blurry or distorted. Now what? Astigmatism can affect anyone — regardless of age. When your eye is curved unevenly, it has problems focusing light and that means blurry vision. Astigmatism is not a disease — it’s completely normal, and more common than you might think.
What Causes Astigmatism?
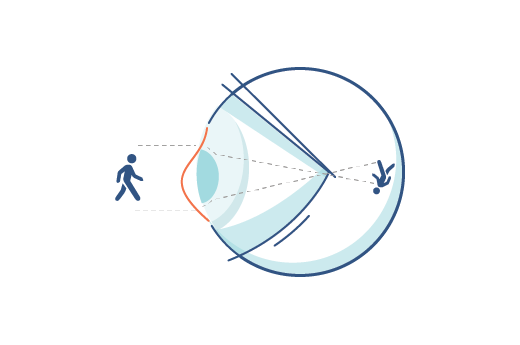
Simply put: your eyeball is supposed to be shaped like a baseball, but astigmatism causes it to be more like a football. You can be born with astigmatism, or you may notice it over time. There are two types of astigmatism: regular and irregular.
Astigmatism Symptoms & Issues
If you can’t quite make out the letters on that street sign or you have to reply to that text in brighter light, you may have astigmatism. If left uncorrected, astigmatism can lead to more severe symptoms, such as headaches, fatigue, squinting and eye-muscle pain.
ACUVUE® BRAND CONTACT LENSES SOLUTIONS
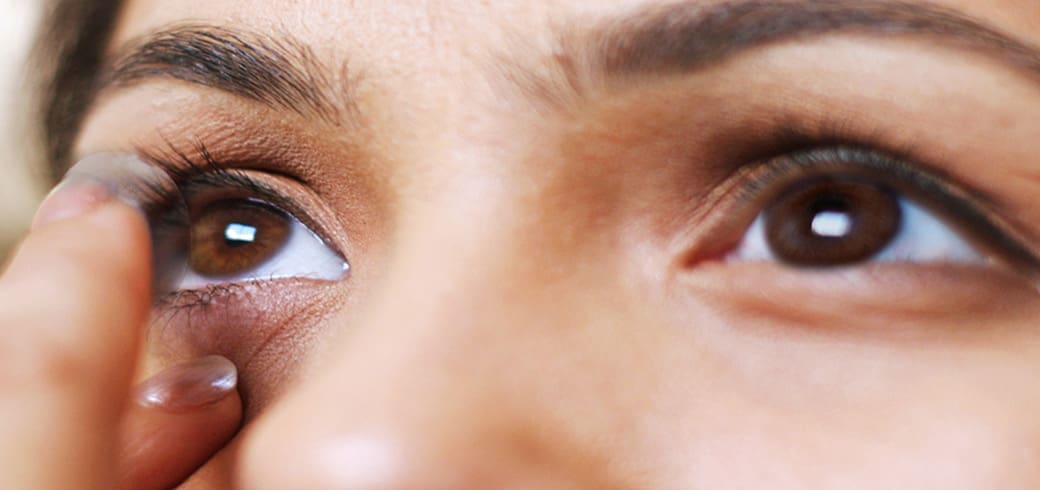
Contacts can offer freedom and flexibility from glasses, and ACUVUE® Brand Contact Lenses for Astigmatism also solve nearsightedness and farsightedness.
Typically, contact lenses can rotate on your eye. For astigmatism, however, it’s especially important that your lenses stay in place for clear vision. Only ACUVUE® Brand Contact Lenses for Astigmatism feature BLINK-STABILIZED™ Design that uses the natural blink of your eye to keep the lens in the right place.
ACUVUE® Brand EYE-INSPIRED™ Design innovations are designed with the latest technology to correct your astigmatism, to help your lenses work with your unique lifestyle needs.
ACUVUE OASYS®1-Day Brand Contact Lenseswith HydraLuxe™ TECHNOLOGY
Experience all-day comfort, vision and handling with our exclusive HydraLuxe™ Technology.
1-DAY ACUVUE®MOIST Brand Contact Lenses for ASTIGMATISM
Get clear, stable vision with the comfort and conveince of a daily disposable lens.
ACUVUE® VITA® for ASTIGMATISM
*Free trial lenses available from participating eye doctors. Exam and fitting fees not included. Subject to retailer.